FEMA
Valuation Service Under FEMA
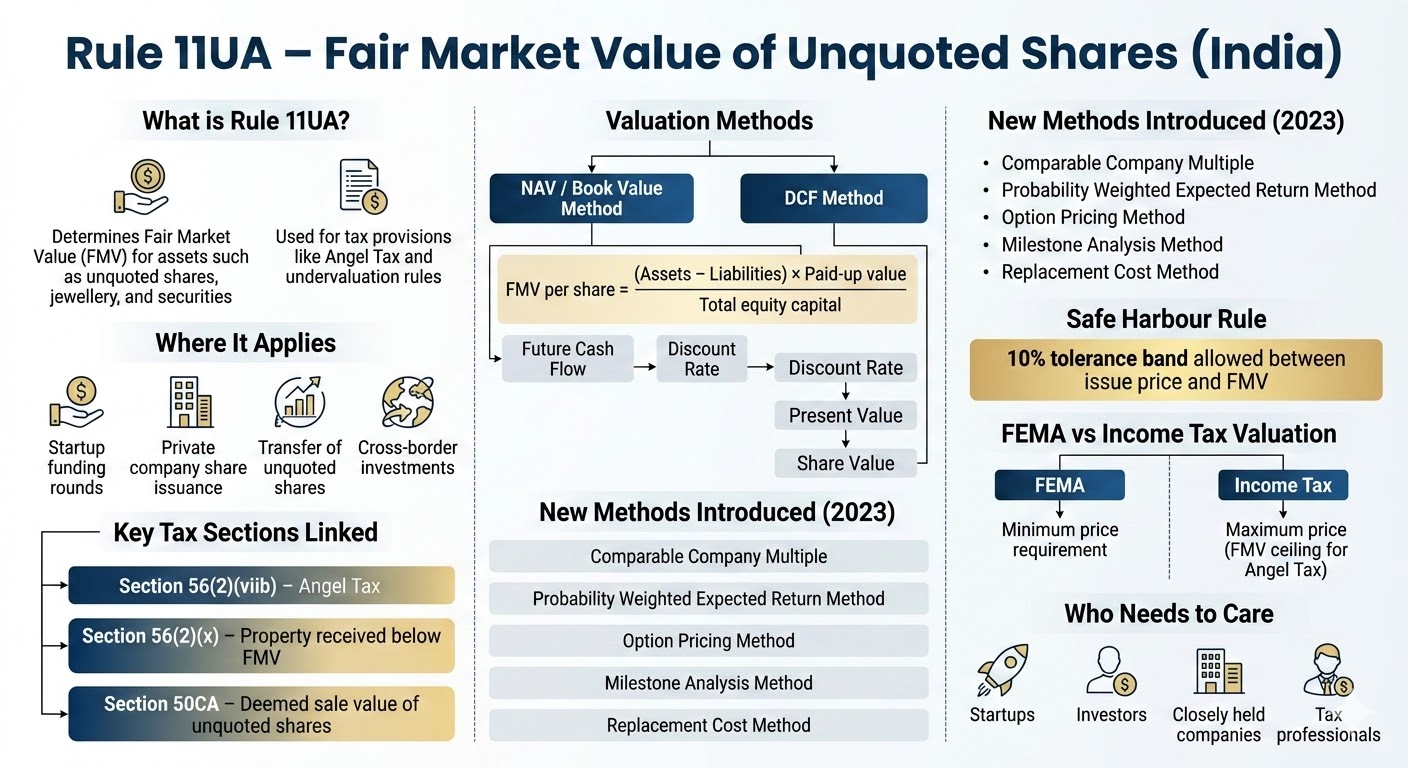
Under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) in India, valuation requirements primarily pertain to cross-border transactions involving the transfer of shares, securities, or assets between Indian residents and non-residents. The objective is to ensure fair pricing and transparency, prevent capital flight, and comply with regulatory guidelines.
Key Valuation Requirements under FEMA:
1. Inbound Investments (FDI)
– 1. When a non-resident invests in an Indian company (e.g., acquiring shares), the price must not be lower than the fair value of the shares.
– 2. Valuation must be conducted by a SEBI-registered merchant banker, a chartered accountant, or as per internationally accepted pricing methods.
2. Outbound Investments (ODI)
When an Indian entity invests abroad (e.g., acquiring shares of a foreign company), the valuation of the foreign entity must comply with:
– 1. Internationally accepted valuation norms for investments in unlisted companies.
– 2. In the case of listed companies, valuation can be based on the stock market price.
3. Transfer of Shares
1. From Resident to Non-Resident:
– The transfer price must not be lower than the fair value determined by valuation.
2. From Non-Resident to Resident:
– The transfer price must not exceed the fair value.
3. Valuation must be performed as per Rule 11UA of Income Tax Rules, 1962 or internationally accepted pricing methods.
4. Compulsory Reporting
- All cross-border transactions involving investments or transfer of securities must be reported to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) through designated forms (e.g., FC-GPR, FC-TRS).
5. Valuation Methods
- FEMA prescribes the use of Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) or other internationally accepted methods, depending on the nature of the asset (e.g., listed/unlisted securities or tangible/intangible assets).
Importance
Valuation under FEMA is critical to:
Valuation under FEMA is critical to:
• Ensure compliance with RBI guidelines.
• Prevent underpricing or overpricing of cross-border transactions.
• Maintain transparency and alignment with global standards in foreign exchange management.
• Prevent underpricing or overpricing of cross-border transactions.
• Maintain transparency and alignment with global standards in foreign exchange management.